Application Architecture - Repository

It is a good practice to separate business logic and data handling. Entity Framework provides an MVC pattern to separate them. However, as the size of a project grows, adding data handling codes directly in the controller file creates duplicate codes and becomes hard to test. A repository pattern is a design pattern that reduces duplication and makes testing easier. Let's see how we can implement a repository pattern in this writing
Project Configurations
Creating a Project with MVC Pattern
Server Architecture - Distributing Projects
Server Structure An interface is a middleman between the browser and the server. It sends a request to a server and handles the response from it. The interface has a dependency on the infrastructure which also has a dependency on the application core proje
jin-co.tistory.com
Implementing MVC Pattern
Application Architecture - MVC
Separation of concern makes our code reusable and easier to manage. In that sense, it is considered a good practice to separate business logic and data handling. MVC pattern is one such implementation that divides an application into three major parts (mod
jin-co.tistory.com
Repository Pattern Configuration
Creating Repository
Add a repository class under the infrastructure folder
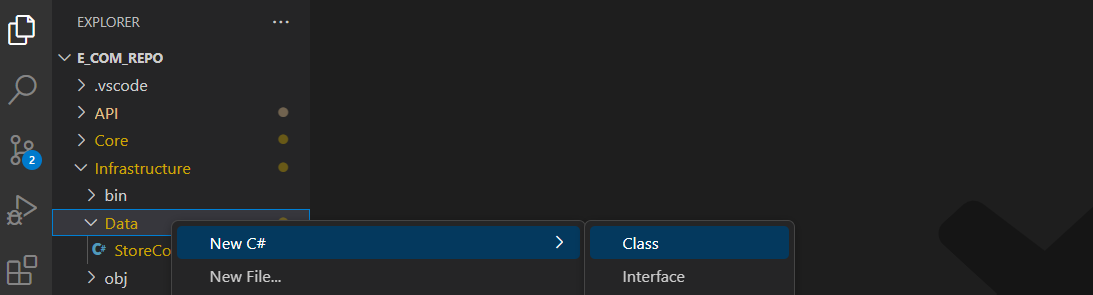
Add constructor and inject context
private readonly StoreContext _context;
public ItemRepo(StoreContext context)
{
this._context = context;
}Add desired methods to handle data
public List<Item> GetItems()
{
return _context.Items.ToList();
}
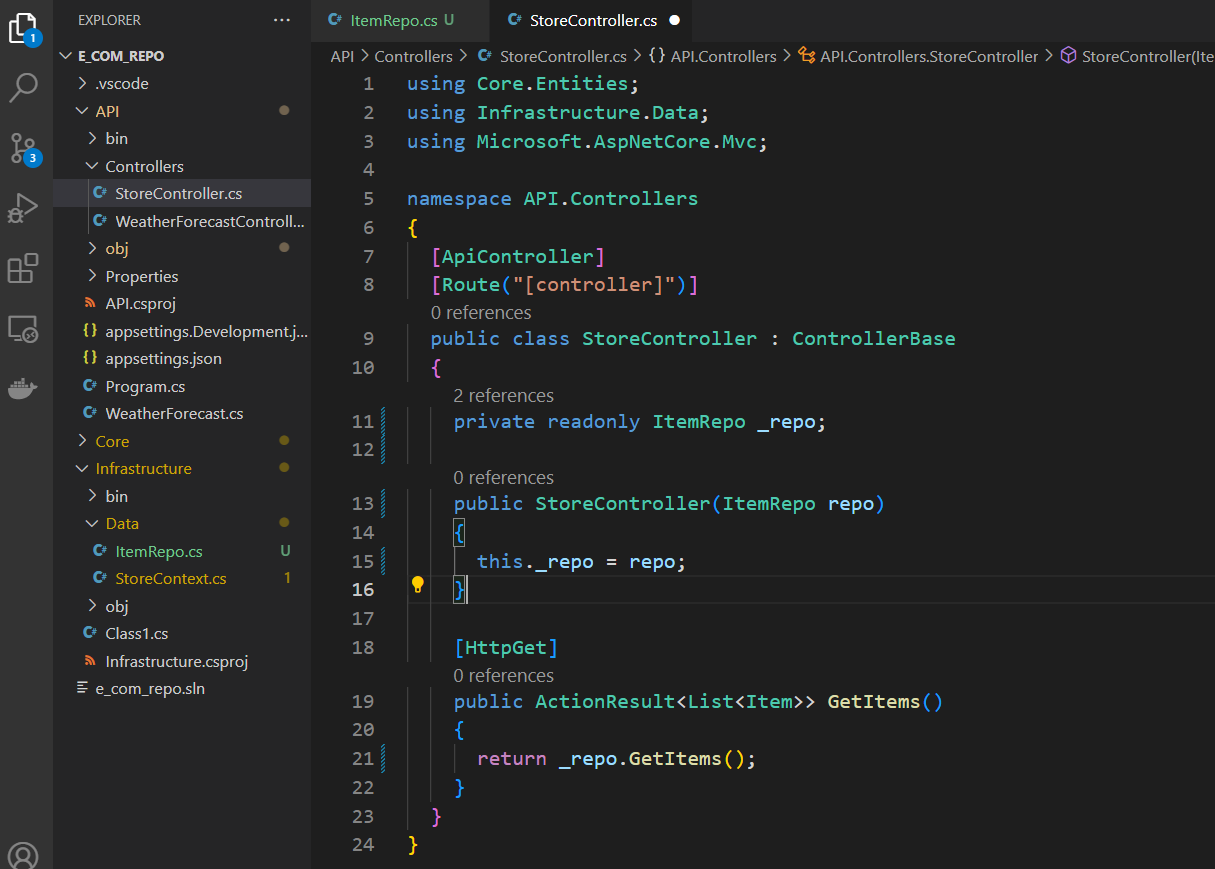
Calling Repository Method in the Controller Class
In a normal MVC pattern, controllers access the context directly as shown below.

To use the repository, delete the context and inject the repository
private readonly ItemRepo _repo;
public StoreController(ItemRepo repo)
{
this._repo = repo;
}Call the method in the HTTP request
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult<List<Item>> GetItems()
{
return _repo.GetItems();
}
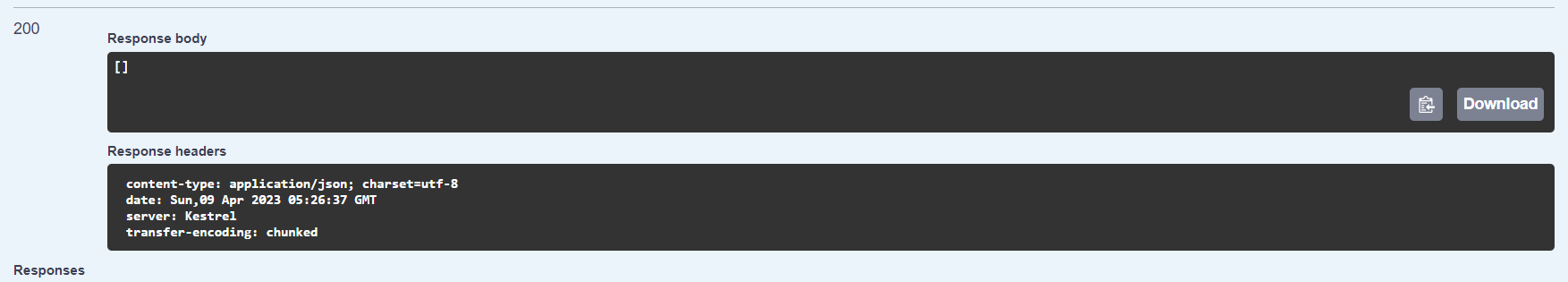
In this writing, we have seen how we can use the MVC repository pattern in .NET with EntityFramework